It’s easy to overlook the importance of wastewater. Clean water flows from a faucet, we utilize it, and then the ‘dirty’ water flows down the drain. This contaminates the water that leaves our homes, schools, and workplaces. In this article we will cover all about wastewater treatment plants.
Most of the citizens’ collected wastewater is then, transported and treated at an urban wastewater treatment plant to eliminate contaminants that are dangerous to the environment and human health before being released back into nature (EEA, 2018). The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals emphasize the importance of access to safe drinking water and sanitation.
In recent decades, massive investments have been made across the world to provide clean water and collect wastewater. We explain how future challenges to providing sustainable water, such as climate change, give new opportunities for resource efficiency and environmental preservation in this briefing.
Key Messages About Waste Water Treatment
- It is hard to collect and treat wastewater in order to protect human health and the environment.
- Wastewater treatment plants around the world have a wide range of situations, including the diverse compounds in sewage, the number of the population served, the requirements of receiving waters, and the local climate.
- While much has been done to provide collection and treatment of wastewater, new pressures such as climate change adaptation, providing facilities in both urban and rural areas, and addressing newly identified pollutants all necessitate significant investment in addition to maintaining existing infrastructure.
- Water efficiency should be promoted because of rising energy costs and scarcity of resources. They also give wastewater treatment more options to contribute to the circular economy, such as through energy generation, water reuse, and material recycling.
Why Do you Need Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP)
In Bangladesh, there are significant economic, public health, and environmental advantages to investing in wastewater treatment infrastructure. Significant progress has been made with the construction of facilities for many Sewage Treatment Plant, but increasing treatment capacity is still necessary to fulfill the demands of the nation’s burgeoning population and protect its water resources.
In order to address environmental pollution and public health issues, wastewater treatment is essential in Bangladesh, particularly in urban areas like Dhaka.
|
Parameter |
Statistic |
Reference |
| Total Sewage Generation in Dhaka |
Approximately 2,000 million liters per day |
|
| Pagla Sewage Treatment Plant Capacity |
120 million liters per day (operating at one-third capacity) |
|
| Percentage of Sewage Treated in Dhaka |
Approximately 20–25% of total sewage |
|
| Planned New Sewage Treatment Plants |
Over 12 large plants in the next 20 years |
|
| Dasherkandi Sewage Treatment Plant Capacity |
500 million liters per day (serving 5 million people) |
Wastewater Treatment Plants
Sewage from our toilets sinks, and washing machines are routed to be treated, reducing disease-causing organisms and the nutrient load that would otherwise pollute the environment and induce development.
Because of the masses of organic matter and nutrients it carries, wastewater from households and industry puts tremendous strain on the aquatic ecosystem. Ammonia and natural processes in streams break down organic debris in the water, but they deplete oxygen, making the river unsuitable for fish and invertebrates.
Excess nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, can cause plants and algae to grow out of control, blocking light and depleting oxygen in the water through respiration or decomposition. During the twentieth century, effective wastewater treatment became widely available, considerably improving human health and environmental quality.
What Are the Various Types of Wastewater Treatment Plants?
Wastewater treatment plants are built to handle, process, and purify sewage. The type of wastewater treatment plant is determined by the wastewater itself. The following three primary types of wastewater treatment plants:
Primary Wastewater Treatment Plant
Primary wastewater treatment plants are those that transform wastewater from various sources into a form that can be used. To separate the waste materials, these plants use a biological and chemical treatment procedure. Following treatment, the water is repurposed for uses like irrigation or municipal water supplies.
Secondary Wastewater Treatment Plant
Dissolved and suspended solids are removed from wastewater at a secondary wastewater treatment facility and subsequently recycled. Compared to primary treatment systems, secondary wastewater treatment plants provide a number of benefits. They handle sewage more effectively, and the cleaned effluent can be applied to industrial or agricultural activities.
Tertiary Wastewater Plant
Tertiary wastewater plants are those that treat wastewater from municipal drainage systems, industrial drainage systems, and agricultural fields. Another name for a tertiary wastewater plant is a tertiary treatment plant or tertiary treatment plant. The treatment and degradation of all harmful pollutants, including chemical substances, microbiological species, and microorganisms, is the major goal of the tertiary wastewater plant.
This will lower the levels of these contaminants in the treated water, making it safe to release it into waterways or the environment. Before wastewater is released into rivers or the environment, the tertiary treatment plant should have the ability to remove extra nutrients and sludge from the wastewater. As a result, the water quality in these places will be improved, and less pollution will enter the rivers, lakes, and oceans.
Benefits of a Wastewater Treatment Plant in Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, the wastewater treatment facilities can be a very valuable investment. A facility that processes wastewater from various sources, including industrial, domestic, agricultural, and others is known as a wastewater plant. It is a powerful factor for developing countries to expand and sustain their economies. The wastewater treatment facility in Bangladesh has a number of benefits, including:
- It helps in maintaining a healthy and clean environment.
- The cleaned water can be used for drinking, cooking, gardening, and other uses.
- Local residents in the area may get jobs thanks to the plant.
- It is a very effective method of disposing of wastewater and saves us from having to dispose of harmful pollutants.
- The money raised from the sale of the wastewater treatment plant can be put toward a number of neighborhood improvement initiatives, which will increase the economic growth.
- Operators of the wastewater treatment plant, engineers, and staff members may receive additional salary from the plant.
- The plant can improve the local communities’ socioeconomic standing, which in turn lowers poverty and improves their general well-being.
- The facility can contribute to a reduction in regional waste production, which lessens the burden on landfills and promotes conservation of resources.
In Bangladesh, there are many businesses with an interest in establishing wastewater treatment plants. These firms may be start-ups or established companies. The fundamental benefit of making an investment in a wastewater treatment plant is that there is little risk and it is likely to be profitable.
Wastewater Treatment Process in Bngladesh
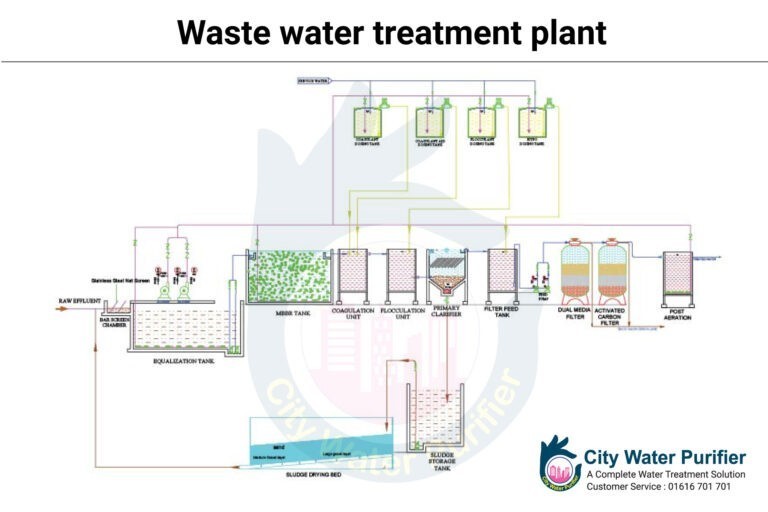
To collect sewage and deliver it to a wastewater treatment plant, sewers must be constructed. Different levels of treatment can be used there, and they usually include:
- Pre-treatment, which physically removes large things like rags and plastics from wastewater, as well as smaller objects like grit. This helps to keep the equipment safe while the treatment progresses.
- The removal of tiny particles is the first step in the treatment process. Heavy sediments sink to the bottom of the wastewater tank, while lighter solids and fat float to the top. The settling and floating components are separated, and the remaining liquid is either discharged to the environment or sent to secondary treatment.
- Secondary treatment, also known as biological treatment, removes any remaining organic debris, suspended solids, bacteria, viruses, and parasites, as well as some nutrients and chemical substances to some extent.
- When discharging into sensitive waters, more thorough treatment is used to eliminate any leftover nutrients. Specific treatment techniques, such as disinfection, can be employed to further remove potentially dangerous bacteria, viruses, and parasites, as well as any lingering chemicals and harmful compounds
Sludge Management
As a by-product of wastewater treatment, sewage sludge is created by bacteria as a result of the consumption of organic contaminants. Sludge can be safely disposed of using a variety of procedures. Liming and aerobic or anaerobic digestion stabilize the sludge, lowering pathogenic organisms and reducing odor.
Dewatering removes superfluous water, reducing the weight and lowering transportation costs, while anaerobic digestion minimizes the amount of sludge and provides biogas. Various disposal options exist, with the majority of them based on national regulatory frameworks and sludge quality. Approximately half of the sewage sludge produced by the EU Member States is used as fertilizer on land, while the other quarter is burnt.
Because sludge can include significant levels of metals, pathogens, and persistent trace organic pollutants, its usage on land may be limited in order to safeguard the environment.
Urban and Rural Wastewater Treatment Provision
It might be difficult to obtain a room in metropolitan areas to build new treatment facilities or upgrade existing ones. Due to noise and various problems, there may be public opposition to buildings near residential areas.
In rural locations, population densities, the nature of the ground and surface water, and the type of collection and treatment system required are all important factors to consider. Individual treatment methods, like septic tanks, are frequently utilized since sewers and treatment are generally expensive and may have a large impact on a few users.
The treatment facility must be able to handle small amounts of water. Furthermore, finding trained employees to operate the treatment facility can be problematic for wastewater treatment plants.
Features of the Wastewater Plant
Wastewater collection: Wastewater is collected from a variety of residential and commercial locations using high-tech equipment such pipes, channels, tanks, etc. Before being discharged back into the environment, wastewater is cleaned up using a variety of treatment techniques as biological decaying, chemical oxidation, oxidation-reduction reactions, or adsorption plants.
Wastewater treatment: The wastewaters are discharged through a variety of systems, including ponds, underground pipes, and open channels.
Flushing of wastewater: Wastewater is flushed down sewers to flush out pollutants that have absorbed into the soil or groundwater. If a wastewater treatment plant’s effluent satisfies specific requirements established by the government, it may be used for irrigation.
Final wastewater disposal: Untreated sewage from wastewater can occasionally be dumped into deep wells or rivers. Additionally, it is heated by burning, which weakens dangerous pollutants.
Maintenance of the wastewater treatment plant: The wastewater treatment plants work better and have a longer lifespan when they are properly maintained. It involves regular inspections of chemicals and machinery, as well as the proper operation of plant equipment.
Operation and management of a wastewater treatment plant: This area is concerned with how a facility is run on a daily basis, including hiring the appropriate staff and getting necessary supplies, among other things.
Inspection and maintenance of the wastewater treatment plant: To guarantee the wastewater treatment plant is operating correctly, routine inspection is required. This involves inspecting factory machinery, chemicals, the handling of pollutants, etc.
Conclusions
We are Bangladesh’s top water treatment plant supplier in Bangladesh for industrial wastewater plants. We have the leading team for wastewater treatment plants. We have more than 10 years of experience in this area. We have all the latest technologies and tools. Our skilled professional’s team is dedicated to giving our customers the best service possible.
We provide wastewater treatment plants services, such as:
- Planning and building facilities for wastewater treatment
- Analyzing and updating current wastewater treatment plants.
- Research and development of cutting-edge wastewater recycling technology
- Creation of cutting-edge wastewater management techniques
- The identification and resolution of environmental problems related to the treatment and disposal of wastewater.

