Soft Water Treatment Plant
Soft Water Treatment Plant: When water contains an excessive amount of calcium and magnesium dissolved in it, it is referred to as “hard water.” The following water issues can be caused by hard water:
- Scale builds up in pipes, causing flow rates to drop.
- Scale builds upon heating and cooling systems, causing higher utility bills and system failures.
- Staining on water taps and a white film on glass surfaces
- Laundry prices have increased as a result of hard water reacting with soap and detergents.
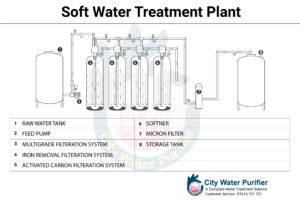
The Water Softening Plants are built to generate treated water for a variety of uses. Throughout the service cycle, treated water is of consistent quality with low residual hardness. The high synthetic resin is utilized to create Calcium and Magnesium ions by exchanging Sodium ions with hardness. After the resin has produced the desired output, it is regenerated with (NaCI) Sodium Chloride solution, and the unit is ready to supply the next batch. The Water Softening Plant units come in a variety of models.
The capacity of the resin utilized for each model is the difference between these models. These units are simple to use and require little maintenance. These types can produce a variety of capacities up to 200 cubic meters per hour.
The Process
The removal of Ca2+ and Mg2+ from a solution or the sequestration of these ions, i.e. binding them to a molecule that prevents them from forming scale or interfering with soaps, are the most common water softening procedures. Ion exchange and precipitation procedures are used to remove the contaminants. The major components of the Water softening system are the mineral tank and the brine tank. A mineral tank and a brine tank make up the water softening system. Water travels through the tank before it may be utilized since the mineral tank and the water supply line are connected. Negatively charged beads or resins attract positively charged calcium and magnesium in the mineral tank.
Calcium and magnesium minerals are deposited on the resin’s surface. The resin is flushed out of the brine tank using a strong sodium (salt) solution. The sodium ions are strong, and they readily overcome the calcium and magnesium ions, driving them off the resins and draining them out of the unit.
Soft Water Operating Principle
A high-capacity polystyrene bead cation exchange resin in sodium form is charged into the Water Softeners. When hard water travels through this resin column, the calcium and magnesium compounds that cause hardness are replaced with sodium salts that have no hardness qualities. This softening process is repeated until the material is depleted of sodium salts, at which point it is regenerated with a common salt solution.
The innovative Co current/counter-current mechanism used in the Water Softener machines assures consistent high-quality treated water.
Pre-filters, a Water Softener Vessel with Resin, a Brine Tank, and other accessories make up a typical water softening plant.
Water softener units are made of a variety of materials, including FRP, LDPE, MS, MS Rubber Lined, and Stainless Steel.
These Water Softeners have Multiport/Diaphragm Valves and are built to provide years of trouble-free service. These Water Softener Units are simple to set up, don’t require any particular foundation, and require very little maintenance.
Water Softener Types
-
Chemical Water Softeners:
Laundry uses chemical softeners. It basically removes magnesium and calcium from garments, extending their lives. It should be noted, however, that the treated water is not suitable for drinking.
-
Water softeners in a box:
Packaged water softeners are really chemicals that are used to soften water. Water softeners come in two varieties: packaged and unpackaged.
There are two types of precipitation: precipitating and non-precipitating.
Precipitating water softeners include things like washing soda and borax. When these compounds react with calcium and magnesium ions, they create an insoluble precipitate. Cleaning efficiency is improved as a result of this. Calcium and magnesium ions are separated from the water in non-precipitating water softeners by complex phosphates.
Features
- Regeneration is done automatically.
- friendly to the user
- Requires less space and uses less energy
- Scales are being reduced
- Pipes and vessels are clogged.
- Improves the efficiency of plumbing and appliance systems.
- prolongs the life of the product
- Compact and light-weight
- Parts that are resistant to corrosion
- Effectively removes hazardous particles.
Advantages
- Simple to set up and use
- Produces water that is gentle and non-scale forming.
- Cation exchange resin with a high capacity.
- Consistently high-quality treated water
- Operating costs are low.
Application
- Feed for the boiler.
- Make-up for the Cooling Tower.
- Plant for air conditioning.
- Textile Processing is a type of textile processing.
- Beverage manufacturing.
- Hospitals, hotels, and laundries are just a few examples.
- Food preparation.
- Textile and chemical.
- Plants that generate electricity using water.
- The plant that produces ice.
- Dyeing methods
- Industries in the pharmaceutical field
- Finishing a product
We Offer
We design and produce high-performance water softeners that effectively reduce water hardness. They aid in the production of zero soft water by removing calcium and magnesium ions from the water through a highly acidic cation exchanger. Our Soft Water Treatment Plant is lightweight and portable, making it simple to relocate from one location to another. It also necessitates less effort in terms of setup and upkeep. We make our products available to our customers at the cheapest price range as one of the leading drinking Water softening plant manufacturers in India.

